Squidの構築
SquidのProxyサーバを何年ぶりくらいに構築することになったので、その時の内容をメモしておきます。
環境
インストール
何はともあれ、squidをインストールしてこないと始まらないので、インストールします。
$ sudo yum -y install squid $ sudo systemctl start squid $ sudo systemctl enable squid $ sudo systemctl list-unit-files -t service | grep squid squid.service enabled
デフォルト設定の確認
squidのコンフィグファイルである /etc/squid/squid.conf を編集して、設定します。まずは、デフォルトファイルの記載の参考に、設定内容を確認していきます。
# # Recommended minimum configuration: # # Example rule allowing access from your local networks. # Adapt to list your (internal) IP networks from where browsing # should be allowed acl localnet src 10.0.0.0/8 # RFC1918 possible internal network acl localnet src 172.16.0.0/12 # RFC1918 possible internal network acl localnet src 192.168.0.0/16 # RFC1918 possible internal network acl localnet src fc00::/7 # RFC 4193 local private network range acl localnet src fe80::/10 # RFC 4291 link-local (directly plugged) machines acl SSL_ports port 443 acl Safe_ports port 80 # http acl Safe_ports port 21 # ftp acl Safe_ports port 443 # https acl Safe_ports port 70 # gopher acl Safe_ports port 210 # wais acl Safe_ports port 1025-65535 # unregistered ports acl Safe_ports port 280 # http-mgmt acl Safe_ports port 488 # gss-http acl Safe_ports port 591 # filemaker acl Safe_ports port 777 # multiling http acl CONNECT method CONNECT # # Recommended minimum Access Permission configuration: # # Deny requests to certain unsafe ports http_access deny !Safe_ports # Deny CONNECT to other than secure SSL ports http_access deny CONNECT !SSL_ports # Only allow cachemgr access from localhost http_access allow localhost manager http_access deny manager # We strongly recommend the following be uncommented to protect innocent # web applications running on the proxy server who think the only # one who can access services on "localhost" is a local user #http_access deny to_localhost # # INSERT YOUR OWN RULE(S) HERE TO ALLOW ACCESS FROM YOUR CLIENTS # # Example rule allowing access from your local networks. # Adapt localnet in the ACL section to list your (internal) IP networks # from where browsing should be allowed http_access allow localnet http_access allow localhost # And finally deny all other access to this proxy http_access deny all # Squid normally listens to port 3128 http_port 3128 # Uncomment and adjust the following to add a disk cache directory. #cache_dir ufs /var/spool/squid 100 16 256 # Leave coredumps in the first cache dir coredump_dir /var/spool/squid # # Add any of your own refresh_pattern entries above these. # refresh_pattern ^ftp: 1440 20% 10080 refresh_pattern ^gopher: 1440 0% 1440 refresh_pattern -i (/cgi-bin/|\?) 0 0% 0 refresh_pattern . 0 20% 4320
設定内容を上から順に確認しつつ、必要項目を変更しています。
ACLタグ
通信が発生するIPアドレス、プロトコルをアクセスリストとして定義する箇所ってことでしょうか。
Squid 3.5.19 Configuration File: acl
acl CONNECT method CONNECT の箇所が、何を定義しているか分からなかったので、調べてみました。これはhttps通信時に利用されるconnectメソッドを定義している場所になります。そもそもProxyサーバを利用したWEBアクセスとは、以下の図のようなものとなります。Proxyサーバが代理でDNS名前解決を行い、実際にアクセスしたいWEBサーバとセッションを貼っている訳です。

Lesson4:HTTPのやりとりを仲介するプロキシを使った流れを知ろう | 日経 xTECH(クロステック)
Proxyサーバが代理として働くために、大元のClientから送られてきたhttp request header内のGET Methodの内容を、Proxyサーバは読むことになります。しかしHTTPS通信の場合、http request header内も暗号化されているため、Proxyサーバは宛先を知ることができません。そこでConnectというMethodを利用します。Connectを利用した場合の通信の流れは、以下の図となります。
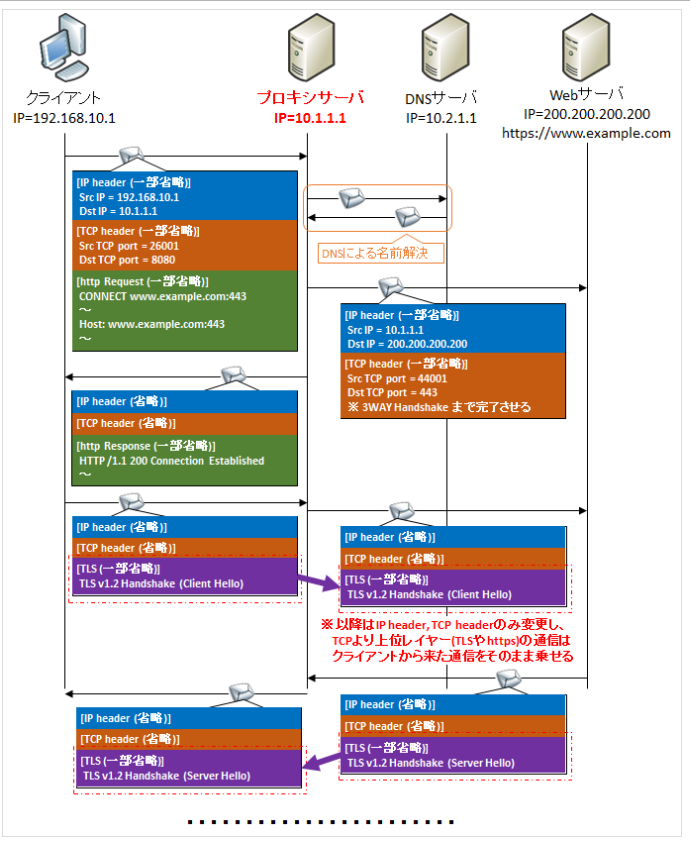
【図解】httpプロキシサーバの仕組み(http GET/https CONNECTメソッド)や必要性・役割・メリットデメリット・DNSの名前解決の順序 | SEの道標
ConnectのMethodは、その名の通りコネクションを貼るだけとなり、実際のデータをやり取りすることはありません。このConnectによりコネクションされたセッションを用いて、大元のClinetとWEBサーバは暗号化されたデータをやり取りすることになります。Proxyサーバは、(当然暗号化されたデータは見れないので、)与えられたデータを横に流すだけとなります。
http_accessタグ
ACLで定義した接続情報に、接続権限(allow/deny)を与える箇所となります。
Squid 3.5.19 Configuration File: http_access
http_access deny to_localhost て何だろと思いましたが、以下とのことです。なるなる。
In other words this blocks attempts to request http://localhost/... on the proxy server via the proxy.
Re: [squid-users] http_access deny to_localhost from Henrik Nordstrom on 2005-01-26 (squid-users)
http_portタグ
Squidが利用するポート番号ですね。
Squid 3.5.19 Configuration File: http_port
cache_dirタグ
Squidでキャッシュされたデータを、ディスクにも保存する場合、利用されることになるディレクトリパスを指定します。ちなみに今回は、キャッシュ機能を利用しないため、コメントアウトしておきます。
Squid 3.5.19 Configuration File: cache_dir
coredump_dirタグ
Squidのコアダンプを、ちゃんと管理したい場合は指定しましょう、って感じでしょうか。
By default Squid leaves core files in the directory from where it was started. If you set 'coredump_dir' to a directory that exists, Squid will chdir() to that directory at startup and coredump files will be left there.
Squid 3.5.19 Configuration File: coredump_dir
refresh_patternタグ
キャッシュに間する設定項目ですね。今回はキャッシュ機能は利用しないので、デフォルトままです。
Squid 3.5.19 Configuration File: refresh_pattern
キャッシュ機能の無効化
今回キャッシュ機能は利用しないので無効化しておきます。手順は公式のwikiに記載されている通りです。バージョンによって異なるようですが、今回のバージョン 3.5.20 では、以下の手順となります。
1.以下をsquid.confに書く
# Squid never cache any response
cache deny all
2.squid.confからcache_dirタグをコメントアウト
デフォルトでコメントアウトされています。
SquidFaq/ConfiguringSquid - Squid Web Proxy Wiki
Squidへの認証処理の追加
Proxyサーバアクセス時にパスワード認証を行いたいので、認証機能を追加しておきます。今回はDigest認証での認証処理を設定します。
1.httpd-toolsのインストール
Digest認証で利用するユーザファイルを作成するために、htdigestコマンドを利用します。htdigestコマンドはhttpd-toolsの中に入っているそうなので、httpd-toolsをインストール。
$ sudo yum install httpd-tools $ which htdigest /usr/bin/htdigest
2. htdigestコマンドにて、ユーザファイルの作成
htdigestコマンドのフォーマットは以下となります。
htdigest passwdfile realm username
realmって何だろとググったら、StackOverflowが教えてくれました。パスワードをhashするために利用される名前空間て感じでしょうか。
Anyway, realm denotes authentication domain for chalenge-response. In the case of digest authentication realm value participates in the password hash, that why it is required when storing password files. See http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc2617#section-3.2.1 for details.
apache - What is realm in htdigest? - Stack Overflow
実際の手順がこちら。ちゃんとハッシュ化してファイルを保存してくれていますね。
$ sudo htdigest -c /etc/squid/password 'MyRealm' 'proxy' Adding password for proxy in realm MyRealm. New password: Re-type new password: $ sudo cat /etc/squid/password proxy:MyRealm:19ccdb75564c555fe23d872cd605edcf
3."squid.conf"の編集
作成した認証情報を、squid.confに設定してあげます。設定には、 auth_parmタグ を利用します。
Squid 3.5.19 Configuration File: auth_param
実際にコンフィグに記載した内容はこちらですね。
auth_param digest program /usr/lib64/squid/digest_file_auth -c /etc/squid/password auth_param digest children 20 startup=0 idle=1 auth_param digest realm MyRealm auth_param digest nonce_garbage_interval 5 minutes auth_param digest nonce_max_duration 30 minutes auth_param digest nonce_max_count 50
それそれのパラメータの意味はこんな感じです。
- auth_param digest program
- 認証処理で利用するモジュールと、パスワードファイルのパスを指定
- -cオプションを付与してあげることで、hash化されたパスワードで利用できるようになります
- auth_param digest children
- 認証処理のプロセスの最大起動数を設定
- auth_param digest realm
- 前段で指定したrealm名を指定
- auth_param digest nonce_garbage_interval
- 暗号処理で利用されるノンスの値の、有効性を確認する間隔
- auth_param digest nonce_max_duration
- ノンスの値の、最大有効時間
- auth_param digest nonce_max_count
- 一度に利用できる最大ノンス値
その他、aclタグとhttp_accessタグで、認証ファイルで指定したユーザを利用できるようにしておきます。
acl digest_ncsa proxy_auth REQUIRED http_access allow digest_ncsa
proxy_auth REQUIRED とすることで、認証ファイルに登録されている全てのユーザが指定されることになります。
接続確認
最後に接続確認して終了です。パスワード認証の有無にてProxy経由でyahooにアクセスしてみます。今回ProxyサーバをAWS上に作成しているので、Proxyサーバは ip-172-31-46-240.ap-northeast-1.compute.internal となっています。
まずはパスワード無しバージョン。接続できていないですね。
$ curl -I -x http://ip-172-31-46-240.ap-northeast-1.compute.internal:3128 -L https://www.yahoo.co.jp/ --proxy-digest HTTP/1.1 407 Proxy Authentication Required Server: squid/3.5.20 Mime-Version: 1.0 Date: Sun, 11 Nov 2018 07:16:46 GMT Content-Type: text/html;charset=utf-8 Content-Length: 3618 X-Squid-Error: ERR_CACHE_ACCESS_DENIED 0 Vary: Accept-Language Content-Language: en Proxy-Authenticate: Digest realm="MyRealm", nonce="XtfnWwAAAAAwgqqfnVUAADbgkmYAAAAA", qop="auth", stale=false X-Cache: MISS from ip-172-31-46-240.ap-northeast-1.compute.internal X-Cache-Lookup: NONE from ip-172-31-46-240.ap-northeast-1.compute.internal:3128 Via: 1.1 ip-172-31-46-240.ap-northeast-1.compute.internal (squid/3.5.20) Connection: keep-alive curl: (56) Received HTTP code 407 from proxy after CONNECT
パスワード有りバージョン。ちゃんと接続できますね。
$ curl -I -U proxy:Passw0rd -x http://ip-172-31-46-240.ap-northeast-1.compute.internal:3128 -L https://www.yahoo.co.jp/ --proxy-digest HTTP/1.1 407 Proxy Authentication Required Server: squid/3.5.20 Mime-Version: 1.0 Date: Sun, 11 Nov 2018 07:17:36 GMT Content-Type: text/html;charset=utf-8 Content-Length: 3618 X-Squid-Error: ERR_CACHE_ACCESS_DENIED 0 Vary: Accept-Language Content-Language: en Proxy-Authenticate: Digest realm="MyRealm", nonce="kNfnWwAAAAAQ12+fnVUAAAiicQwAAAAA", qop="auth", stale=false X-Cache: MISS from ip-172-31-46-240.ap-northeast-1.compute.internal X-Cache-Lookup: NONE from ip-172-31-46-240.ap-northeast-1.compute.internal:3128 Via: 1.1 ip-172-31-46-240.ap-northeast-1.compute.internal (squid/3.5.20) Connection: keep-alive HTTP/1.1 200 Connection established HTTP/2 200 date: Sun, 11 Nov 2018 07:17:36 GMT p3p: policyref="http://privacy.yahoo.co.jp/w3c/p3p_jp.xml", CP="CAO DSP COR CUR ADM DEV TAI PSA PSD IVAi IVDi CONi TELo OTPi OUR DELi SAMi OTRi UNRi PUBi IND PHY ONL UNI PUR FIN COM NAV INT DEM CNT STA POL HEA PRE GOV" x-content-type-options: nosniff x-xss-protection: 1; mode=block x-frame-options: SAMEORIGIN expires: -1 pragma: no-cache cache-control: private, no-cache, no-store, must-revalidate x-xrds-location: https://open.login.yahooapis.jp/openid20/www.yahoo.co.jp/xrds content-type: text/html; charset=UTF-8 age: 0 via: http/1.1 edge2561.img.umd.yahoo.co.jp (ApacheTrafficServer [c sSf ]) server: ATS set-cookie: TLS=v=1.2&r=1; path=/; domain=.yahoo.co.jp; Secure
ログファイル関連
Squidのアクセスログは /var/log/squid/access.log に吐かれます。今回の方法でSquidをインストールした場合(パッケージから入れた場合)、logrotateの設定が自動で入るので、特に考慮は不要となります。以下は、デフォルトのlogrotateの設定です。
$ sudo cat /etc/logrotate.d/squid /var/log/squid/*.log { weekly rotate 5 compress notifempty missingok nocreate sharedscripts postrotate # Asks squid to reopen its logs. (logfile_rotate 0 is set in squid.conf) # errors redirected to make it silent if squid is not running /usr/sbin/squid -k rotate 2>/dev/null # Wait a little to allow Squid to catch up before the logs is compressed sleep 1 endscript }
作成されたsquid.conf
最終的に出来上がったsuid.confファイルを貼っておきます。
# # Recommended minimum configuration: # # Example rule allowing access from your local networks. # Adapt to list your (internal) IP networks from where browsing # should be allowed acl localnet src 10.0.0.0/8 # RFC1918 possible internal network acl localnet src 172.16.0.0/12 # RFC1918 possible internal network acl localnet src 192.168.0.0/16 # RFC1918 possible internal network acl localnet src fc00::/7 # RFC 4193 local private network range acl localnet src fe80::/10 # RFC 4291 link-local (directly plugged) machines acl SSL_ports port 443 acl Safe_ports port 80 # http acl Safe_ports port 21 # ftp acl Safe_ports port 443 # https acl Safe_ports port 70 # gopher acl Safe_ports port 210 # wais acl Safe_ports port 1025-65535 # unregistered ports acl Safe_ports port 280 # http-mgmt acl Safe_ports port 488 # gss-http acl Safe_ports port 591 # filemaker acl Safe_ports port 777 # multiling http acl CONNECT method CONNECT # # Recommended minimum Access Permission configuration: # # Deny requests to certain unsafe ports http_access deny !Safe_ports # Deny CONNECT to other than secure SSL ports http_access deny CONNECT !SSL_ports # Only allow cachemgr access from localhost http_access allow localhost manager http_access deny manager # We strongly recommend the following be uncommented to protect innocent # web applications running on the proxy server who think the only # one who can access services on "localhost" is a local user #http_access deny to_localhost # # INSERT YOUR OWN RULE(S) HERE TO ALLOW ACCESS FROM YOUR CLIENTS # auth_param digest program /usr/lib64/squid/digest_file_auth -c /etc/squid/password auth_param digest children 20 startup=0 idle=1 auth_param digest realm MyRealm auth_param digest nonce_garbage_interval 5 minutes auth_param digest nonce_max_duration 30 minutes auth_param digest nonce_max_count 50 acl digest_ncsa proxy_auth REQUIRED http_access allow digest_ncsa # Example rule allowing access from your local networks. # Adapt localnet in the ACL section to list your (internal) IP networks # from where browsing should be allowed http_access allow localnet http_access allow localhost # And finally deny all other access to this proxy http_access deny all # Squid normally listens to port 3128 http_port 3128 # Uncomment and adjust the following to add a disk cache directory. #cache_dir ufs /var/spool/squid 100 16 256 # Leave coredumps in the first cache dir coredump_dir /var/spool/squid # # Add any of your own refresh_pattern entries above these. # refresh_pattern ^ftp: 1440 20% 10080 refresh_pattern ^gopher: 1440 0% 1440 refresh_pattern -i (/cgi-bin/|\?) 0 0% 0 refresh_pattern . 0 20% 4320 # Squid never cache any response cache deny all